
Thanks to cutting-edge research in fields as diverse as mathematics, physics, biological and medical sciences, engineering, and humanities and social sciences, Paris-Saclay is attracting a growing number of students and businesses to develop multiple technologies. We believe that many of these technologies could be used for the benefit of patients and that the essential condition for this judicious use is the dialogue between the research communities, the healthcare world and the manufacturers. PASREL, anchored in the Paris-Saclay University, wants to foster and encourage this dialogue for the benefit of all.
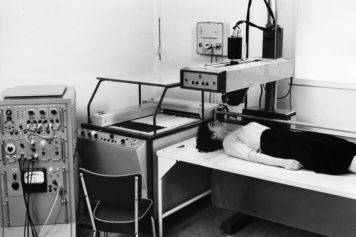
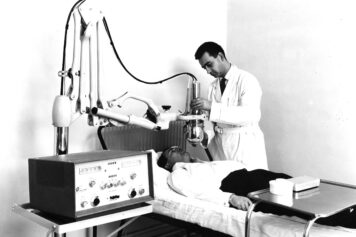
A proven model for clinical and industrial transfer in the field of medical imaging.
In 1934, Frédéric Joliot and his wife, Irène Joliot-Curie, discovered artificial radioactivity. Quickly convinced of the tremendous interest of these chemical species in biology and medicine, they announced in 1935, when they received their Nobel Prize, that radioelements could be used to describe many functions of the organism. The synthesis of radioactive species was to allow the development of a new science: medical imaging. After becoming the first Haut Commissaire of the CEA in 1946, Frédéric Joliot decided to bring biology to the CEA.
In 1948 and 1953, the first laboratories for lifescience research were set up in Fontenay-aux-Roses and Saclay. Their work was essentially focused on the use of radioelements as tracers. Created in 1958, within the Orsay hospital, the Frédéric Joliot Hospital Service (SHFJ, that currently belongs to the Frederic Joliot Institute for Life Sciences) was the specialist in this field.
Since 1958, thanks to its dual affiliation with a hospital and the CEA and to its expertise covering the whole chain of medical imaging, the SHFJ has never ceased to transfer advances in fundamental research into clinical applications.
It is this successful model of clinical and industrial transfer in the field of medical imaging that PASREL wants to extend to all health technologies.


A broad interdisciplinary network to develop technological and organizational innovations for the benefit of patients and caregivers.
Created in January 2020, Université Paris-Saclay is composed of :
Université Paris-Saclay offers an exceptional, multidisciplinary environment, with strong skills in mathematics, physics, chemistry, engineering sciences, software technologies, data sciences, life sciences and human and social sciences.
Interdisciplinarity is at the heart of PASREL: firstly, because it is a source of creativity and innovation; and secondly, because PASREL aims to connect disciplines that are often far apart (engineering sciences, social sciences, medicine, biology, etc.). PASREL contributes to the structuring of the Université Paris-Saclay by running an interdisciplinary program, the Hub PASREL, positioned across 6 of the University's Graduate Schools.


In 2027, the PASREL building will be built in the immediate vicinity of the new Paris-Saclay Hospital (GHNE). A genuine collaborative platform, it will be dedicated to the integration of innovation in the hospital environment.
The EPAPS, a public body for the development of the Paris-Saclay area, is responsible for planning and coordinating the development of the scientific and technological cluster on the Saclay plateau. It is in charge of developing the Corbeville neighborhood where a new hospital, the Paris-Saclay Hospital, opened in June 2024.
In the immediate vicinity of this hospital, the PASREL building will be built in 2027. It will be an open collaborative platform dedicated to the integration of innovation in the hospital environment. The PASREL building will be a showcase for medical technologies developed in Paris-Saclay by: